By: Nilesh Jain
|
Published on: July 26, 2024
What is Software Testing?.
Software testing is a method used to evaluate and verify that a
software
application or system meets the specified requirements.
It involves running the software or system components using either
manual
methods or automated tools to assess various properties or features.
The primary purpose of software testing is to identify bugs, gaps,
or
missing
requirements contrary to the actual requirements.
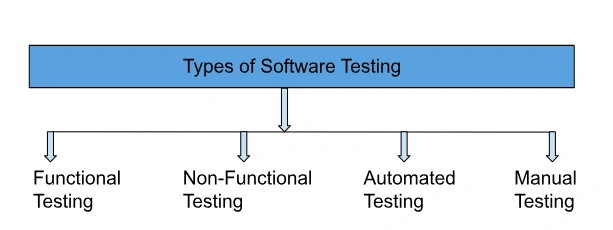
Types of Software Testing
Software testing can be categorized into various types, each serving a unique
purpose-
-
Functional Testing: Ensures that the software system meets the
specified functional requirements and performs as intended.
-
Non-Functional Testing: Evaluates non-functional characteristics
such as performance, usability, and reliability.
-
Automated Testing: Uses automated tools to execute tests and
compare actual outcomes with predicted outcomes.
-
Manual Testing: Requires human involvement to carry out test
cases manually, without utilizing automation tools.
Why is Software Testing Important?
Ensure Software Quality and Reliability
The main objective of software testing is to guarantee the software's
quality
and dependability. By identifying and fixing defects early, testing helps prevent the
occurrence
of critical issues in the production environment, thus enhancing the software's
reliability.
Enhancing User Experience and Trust
Quality software leads to a better user experience, which in turn builds trust
and satisfaction among users. Testing ensures that the software performs well under various
conditions, providing a seamless experience for the end-users.
Benefits of Software Testing in the Development Lifecycle
Software testing encompasses several specific aspects, including:
-
Early Bug Detection and Fixing: Identifying bugs early in the
development process saves time and cost compared to fixing issues later in the
lifecycle.
-
Improved Software Quality:Continuous testing ensures that the
software meets the required standards and functions as expected.
-
Risk Mitigation: Testing helps identify potential risks and
vulnerabilities, enabling the team to address them before deployment.
-
Cost Efficiency: Preventing major issues early reduces the cost
of fixing bugs and ensures that the project stays within budget.
What are Some Specific Aspects of Software Testing?
Software testing encompasses several specific
aspects,
including:
- Unit Testing: Concentrates on testing separate parts or modules of the
software
to
verify they operate as intended.
- Integration Testing: Verifies that different modules or services used by the
application interact correctly.
- System Testing: Evaluate the complete and integrated software to ensure it
meets
the
specified requirements.
- Acceptance Testing: Conducted to determine if the system satisfies the
acceptance
criteria and is ready for deployment.
What are the Key Aspects of Software Testing?
The key aspects of software testing include:
-
Test Planning: Defining the objectives and scope of testing.
-
Test Design: Creating test cases and test data.
-
Test Execution: Running the tests and recording the results.
-
Test Reporting: Documenting the findings and providing feedback to the
development team.
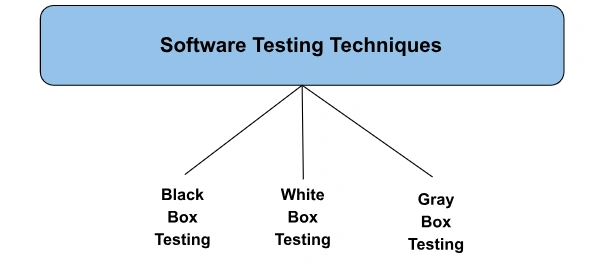
What are the Common Software Testing Techniques?
Common software testing techniques include -
-
Black Box Testing: Performing tests without any understanding of the internal
structure or code of the application.
-
White Box Testing: Creating test cases and test data.
-
Gray Box Testing: A blend of both black box and white box testing methods.
Tools Used in Software Testing
Selecting the right tools for software testing is essential for ensuring the
efficiency and effectiveness of the testing process. Below are detailed descriptions of some
widely-used software testing tools:
Selenium
Selenium is an open-source tool that is widely used for automating web
application testing. It supports multiple browsers and platforms, including Windows, Mac, and
Linux. Selenium allows testers to write test scripts in various programming languages such as
Java, C#, Python, and Ruby. It includes components like WebDriver, Selenium Grid, and Selenium
IDE, which enable parallel test execution, enhance test performance, and provide a user-friendly
interface for creating automated tests.
JIRA
JIRA is a versatile tool primarily used for bug tracking, issue tracking, and project
management. Developed by Atlassian, JIRA helps teams plan, track, and manage agile software
development projects. It integrates seamlessly with other tools such as Confluence and
Bitbucket, allowing for a cohesive workflow. JIRA's robust reporting features enable teams to
monitor project progress, manage backlogs, and ensure timely resolution of issues.
TestComplete
TestComplete is a comprehensive automated testing tool that supports desktop, web, and mobile
applications. It offers an intuitive record-and-playback feature, making it accessible for
testers with varying levels of expertise. TestComplete supports a wide range of scripting
languages, including JavaScript, Python, and VBScript. Its powerful object recognition engine
ensures that tests are stable and reliable, even when the application's user interface changes.
Postman
Postman is an ideal tool for API testing, allowing developers and testers to design, test, and
document APIs efficiently. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and executing API
requests, and its automated testing capabilities enable the creation of comprehensive test
suites. Postman's collaboration features facilitate teamwork by enabling the sharing of
collections and environments. It also offers integrations with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, making
it an essential tool for continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
Appium
Appium is an open-source tool for automating mobile application testing on both iOS and Android
platforms. It supports a variety of programming languages, including Java, JavaScript, and
Python. Appium allows for cross-platform testing by using the same test script to test
applications on different platforms. Its architecture is built on top of the WebDriver protocol,
ensuring compatibility with Selenium, which simplifies the transition from web to mobile
testing.
LoadRunner
LoadRunner, developed by Micro Focus, is used for performance testing to simulate thousands of
users and monitor system behavior. It helps identify and resolve performance bottlenecks by
generating real-world load scenarios. LoadRunner supports a wide range of protocols, including
HTTP, HTTPS, SOAP, and FTP. Its powerful analysis and reporting tools provide detailed insights
into system performance, enabling teams to optimize their applications for scalability and
reliability.
Importance of Finding the Best Testing Tool
Choosing the right testing tool is crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of the testing
process. The right tools can streamline testing efforts, reduce manual work, and improve
accuracy.
Factors to be Considered While Selecting a Software Testing Tool
-
Ease of Use: The tool should be user-friendly and easy to learn.
-
Compatibility: It should be compatible with the technology stack used in the
project.
-
Cost: Consider the budget and the cost of the tool.
-
Support and Community: A tool with good support and an active community can be
very beneficial.
What are the Helpful Software Testing Tools?
-
Selenium: An open-source tool for automated testing of web applications.
-
JIRA: A tool for bug tracking and project management.
-
TestComplete: A comprehensive automated testing tool for desktop, web, and mobile
applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Software testing is integral to the SDLC, ensuring that the
software meets quality standards and is free of defects before
deployment.
Testing should be integrated as early as possible, ideally from
the requirements phase, to identify and address issues early.
Automated testing can save time, reduce human error, and
increase test coverage, making it more efficient than manual
testing.